The Navy's AEGIS Combat System (ACS)
The term AEGIS in the ancient Greek language means "protective shield".
|
The ACS is based on the concept of Cooperative Engagement Capability (CEC)
This capability comes from a centralized, automated, command-and-control (C2),
weapons control system with a series of networked sensors and communications.
It is designed as a total weapons system from start to end as follows:
* networked local and worldwide communications
* target detection and identification
* establishing a track
* threat analysis
* weapons assignment
* target kill
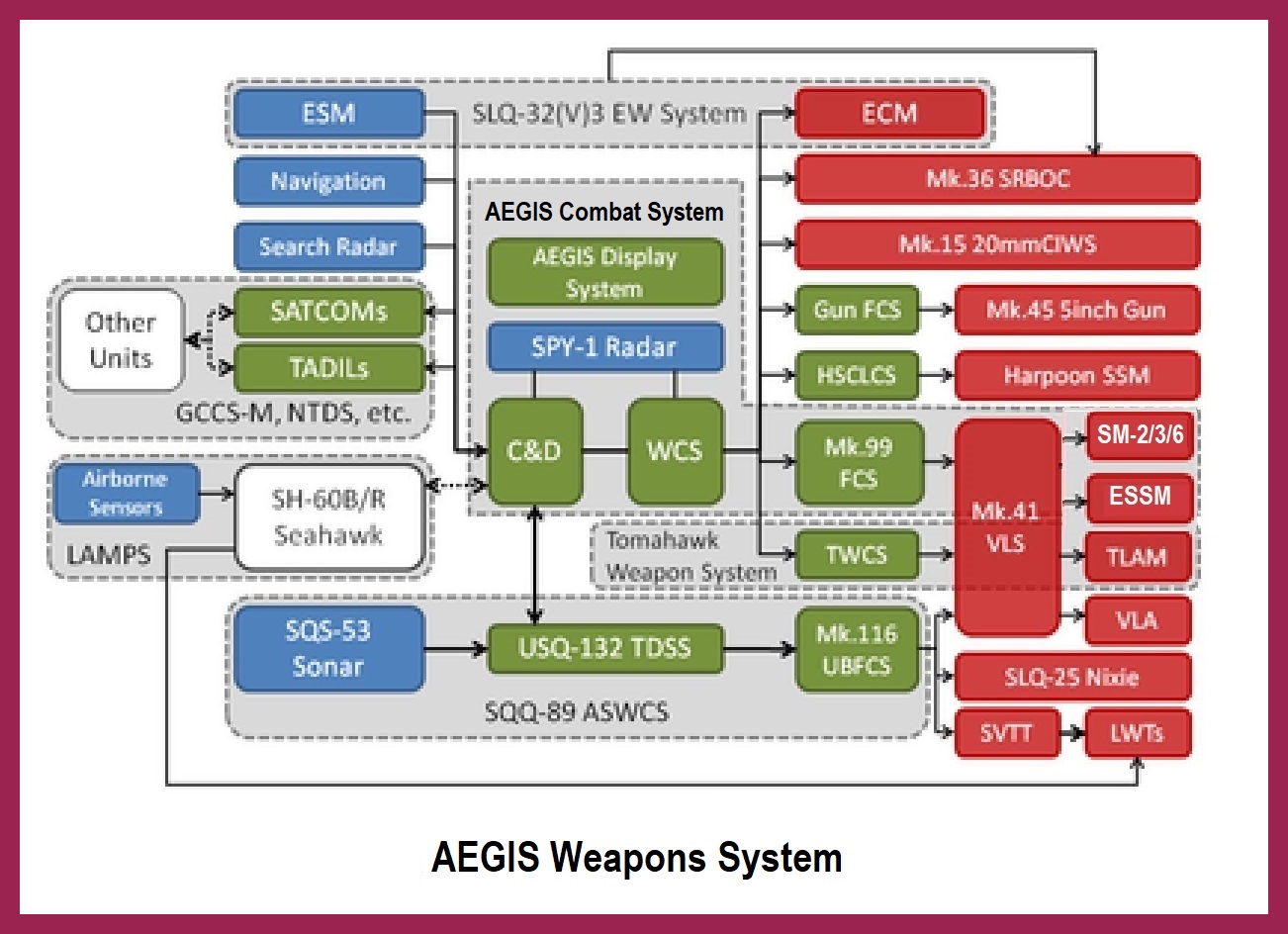
The major ACS components are as follows:
* AN/SPY-1 radar (the centerpiece)
* MK-99 Fire Control System
* Weapons Control System (WCS)
* Command & Decision Suite (C&D)
* AN/SQQ-89 ASW Control System (ASWCS)
* MK-41 Vertical Launch Sustem (VLS)
* Close-In Weapons System (CIWS)
* The ship's missile complement including the SM2, SM-3, SM-6, and ESSM
The MK-99 Fire Control System contains multiple AN/SPG-62 illuminator radars which
provide semi-active homing terminal missile guidance to the ESSMs and standard missiles
(excluding SM-3s). New versions of the SM-2, SM-6, and ESSM missiles have
active mode seekers, and when fired, they do not require illuminator radars.
The centerpiece of the Navy's ACS system is currently the AN/SPY-1 radar, an advanced,
three dimensional, electronically scanned, automatic detect and track, multi-function
phased-array radar. This high-powered radar (6 megawatts) is able to perform search, track and
missile guidance functions simultaneously. It provides mid-course guidance via a data uplink to
the missiles. It has a track capacity of more than 100 targets.

|
The AEGIS Weapons System is currently installed on only two classes of U.S. Navy
ships as follows:
* Ticonderoga Class Cruisers (CG-52 Class); some, but not all
* Arleigh Burke Class Destroyers (DDG-51 Class); many, but not all
* As of December 2020, 41 ships have the AEGIS Weapons System installed
The first Flight III version of the Arleigh Burke Class Destroyers (the U.S.S. Jack H. Lucas
DDG-125) is currently under construction, and will be the first AEGIS ship equipped with
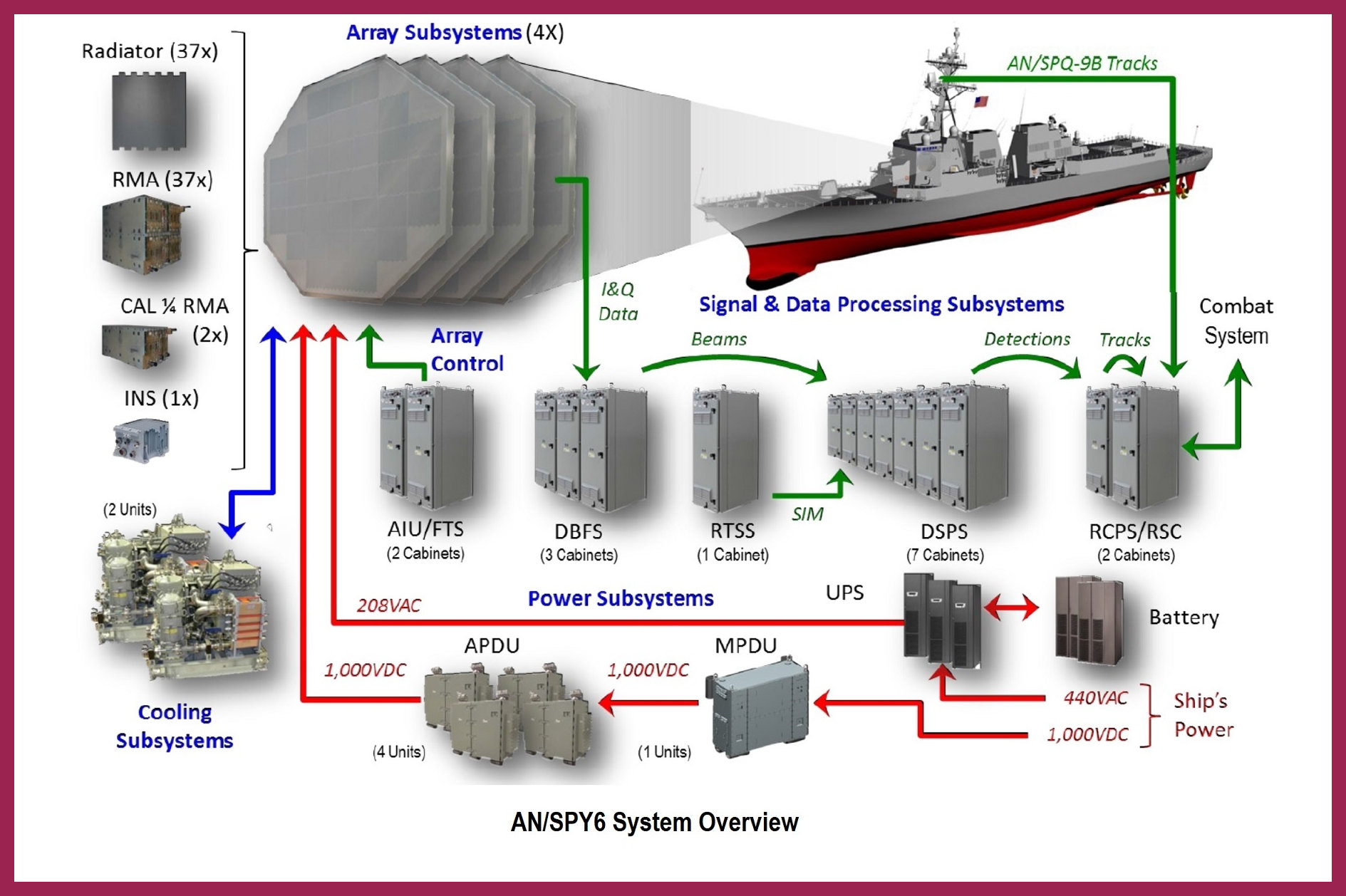
the Advanced Missile Defense Radar (AMDR AN/SPY-6) as the system centerpiece. This
new phased-array radar is built from radar module assemblies (RMAs), and can be scaled
down or up to fit the space and power restrictions of a respective ship. Currently, at 148
RMAs (4 faces x 37 RMAs per face), the AN/SPY-6 for the new Flight III version of the
DDGs, is capable of outperforming the current SPY-1 radar by acquiring targets of half the
size at twice the distance.
|
The sensitivity feature, in conjunction with the following other weapons
system feartures will make the Arleigh Burke Class ships formidable war
fighting machines:
* MK41 Vertical Launch System (VLS)
* the current array of available missiles and missile guidance
* advanced undersea and surface warfare systems
* Close-In Weapons System (CIWS)
* guns
* embarked sea-control helicopters
The Navy has already developed plans to backfit some of the older Flight II and
Flight IIA Arleigh Burke Class ships with scaled-back versions of the SPY-6 AMDR
where appropriate. As the Ticondera Class cruisers get older, the Navy expects to
replace them with Flight III Arleigh Burke Class destroyers before decommissioning
them.
More information from Raytheon on the AMDR follows:

|